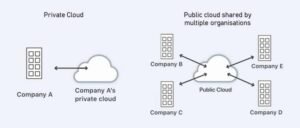
Private cloud deployment models
Private cloud deployment models involve the exclusive use of computing resources by a single organization. These models provide organizations with greater control, customization, and security compared to public clouds. There are different types of private cloud deployment models, including on-premises private cloud and externally hosted private cloud.
On-Premises Private Cloud deployment
The private cloud infrastructure is deployed and maintained within the organization’s own data centers. This approach provides maximum control over the hardware, networking, and security.
An on-premises private cloud refers to a cloud computing environment that is deployed and maintained within an organization’s own physical data centers, rather than relying on external cloud service providers. In this model, the organization owns, manages, and operates the entire private cloud infrastructure, including servers, storage, networking equipment, and virtualization technologies.
The organization owns, operates, and maintains the entire private cloud infrastructure, giving it maximum control over hardware, software, and configurations. Complete control allows organizations to tailor the environment to specific security, compliance, and performance requirements.
On-premises private clouds offer a high degree of customization, enabling organizations to design and configure the infrastructure according to their unique needs and preferences. On-premises private clouds are often chosen by organizations with strict security and compliance requirements, as they provide direct oversight and control over sensitive data.
Proximity to on-premises resources can result in low-latency access, which is crucial for applications that demand high performance. Organizations can ensure data residency and compliance with data sovereignty regulations by keeping data within their own physical facilities. On-premises private clouds typically involve substantial upfront capital expenditures for hardware, networking, and infrastructure. Ongoing operational costs include maintenance, power, and cooling.
Scaling on-premises private cloud infrastructure can be more complex and time-consuming compared to public cloud solutions. Organizations need to plan for future capacity requirements.
Advantages: Full control, customization, and the ability to meet specific security and compliance requirements.
Considerations: Requires significant upfront capital investment and ongoing maintenance costs.
Managed Private Cloud deployment
The organization partners with a third-party service provider to host and manage the private cloud infrastructure. The provider is responsible for hardware maintenance, updates, and operational tasks.
A managed private cloud is a cloud computing solution where a third-party service provider offers hosting, maintenance, and management services for a dedicated private cloud infrastructure. In this model, the organization retains ownership and control over its data, applications, and configurations within the private cloud, while the service provider takes care of infrastructure-related tasks
The service provider is responsible for the setup, maintenance, monitoring, and management of the private cloud infrastructure. This includes hardware provisioning, software updates, security, and overall operational tasks. The organization owns its data and applications within the private cloud, maintaining control over configurations and security policies. Outsourcing the management of the private cloud infrastructure can lead to cost savings for the organization, as it doesn’t have to invest in and manage its own physical hardware.
By relying on a specialized service provider for infrastructure management, the organization can focus more on its core business activities, innovation, and strategic goals. While the organization maintains control over its data and applications, there may be some limitations on customization compared to an on-premises private cloud. The level of control can vary based on the service provider’s offerings. Managed private clouds can be designed to meet specific security and compliance requirements. The service provider often has expertise in implementing and maintaining robust security measures.
Managed private clouds can offer scalability, allowing organizations to scale resources up or down based on changing needs. This is typically more flexible than traditional on-premises solutions. Service providers are experienced in optimizing resource usage, ensuring efficient performance and reducing the risk of underutilization or overprovisioning. Managed private cloud services often include additional managed services, such as automated backups, disaster recovery, and 24/7 support, enhancing the overall reliability of the infrastructure.
Organizations should establish clear SLAs with the service provider, defining performance expectations, availability, and other critical metrics to ensure the desired level of service. Some organizations choose to integrate a managed private cloud with public cloud services in a hybrid cloud model, providing a balance between control and scalability. Managed private clouds are particularly beneficial for organizations that want the advantages of a private cloud environment without the burden of managing the underlying infrastructure. This model allows organizations to leverage the expertise of a service provider while maintaining control over their data and applications. It is essential for organizations to carefully evaluate service providers and define clear expectations through service level agreements.
Advantages: Offloads operational tasks to a specialized provider, cost savings compared to on-premises infrastructure.
Considerations: May have slightly less control over infrastructure compared to on-premises, reliance on the service provider.
Hosted Private Cloud deployment
Similar to a managed private cloud, but the infrastructure is hosted in a third-party data center. The organization retains control over the virtualized environment and applications.
A hosted private cloud is a cloud computing environment in which a third-party service provider hosts and manages a dedicated private cloud infrastructure for a single organization. In this model, the organization’s computing resources, including servers, storage, and networking, are deployed and operated on infrastructure provided by the hosting service. The private cloud infrastructure is hosted in data centers owned and operated by a third-party service provider.
Outsourcing the hosting allows the organization to leverage the provider’s infrastructure without managing physical data center facilities. While the organization doesn’t own the physical infrastructure, it retains ownership and control over its data, applications, and configurations within the private cloud. Hosting with a third-party provider can result in cost savings compared to maintaining an on-premises data center. The organization avoids upfront capital expenditures for hardware.
The organization can focus on its core business activities, leaving the hosting and management of the infrastructure to a specialized service provider. Customization options may vary depending on the hosting provider. While the organization maintains control over its data and applications, there may be some limitations on customization. Hosted private clouds can be designed to meet specific security and compliance requirements. The hosting provider often implements security measures and conducts audits.
Hosted private clouds can offer scalability, allowing organizations to scale resources up or down based on changing needs. This is typically more flexible than traditional on-premises solutions. Hosting providers are experienced in optimizing resource usage, ensuring efficient performance and reducing the risk of underutilization or overprovisioning. Hosted private cloud services often include additional managed services, such as automated backups, disaster recovery, and 24/7 support, enhancing the overall reliability of the infrastructure.
Organizations should establish clear SLAs with the hosting provider, defining performance expectations, availability, and other critical metrics to ensure the desired level of service. Some organizations choose to integrate a hosted private cloud with public cloud services in a hybrid cloud model, providing a balance between control and scalability. Hosted private cloud deployment offer organizations the benefits of a private cloud environment while alleviating the responsibilities of physical infrastructure management. This model is particularly suitable for organizations that prefer a dedicated environment but want to leverage the expertise and infrastructure of a hosting provider. It is important for organizations to carefully evaluate hosting providers and ensure that the services align with their specific requirements.
Advantages: Outsourcing infrastructure management while maintaining control, flexibility in resource allocation.
Considerations: Relies on the hosting provider’s infrastructure and services.
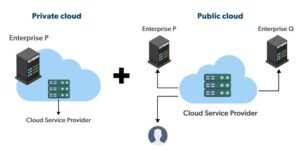
Virtual Private Cloud deployment (VPC)
A subset of a public cloud infrastructure is reserved and isolated for a single organization. While it is part of a public cloud, it is logically segregated for private use.
A Virtual Private Cloud (VPC) is a cloud computing environment that provides a logically isolated and customizable section of a public cloud infrastructure. In a VPC, users can deploy virtualized resources such as virtual machines, storage, and networking components within their dedicated and private space. It offers a way to enjoy the benefits of the cloud, such as scalability and flexibility, while maintaining control and isolation. A VPC logically isolates the resources and networking components within a shared public cloud infrastructure. This isolation provides a dedicated space for an organization’s virtualized assets.
Users have control over the configuration of the VPC, allowing them to define their own IP address range, create subnets, and configure network gateways. This customization facilitates the alignment of the cloud environment with specific organizational needs. VPCs include features such as network access controls, firewalls, and security groups, enabling users to define and control access to resources. This contributes to the overall security of the cloud environment.
VPCs are designed to be scalable, allowing users to scale resources up or down based on demand. This scalability supports dynamic workloads and changing resource requirements. VPCs can be integrated with public cloud services, enabling users to benefit from both the isolation of a private environment and the scalability of public cloud resources. This is often associated with a hybrid cloud strategy. VPCs enable efficient utilization of resources, and users only pay for the resources they consume. This can result in cost savings compared to traditional on-premises infrastructure.
Public cloud providers offering VPCs often have data centers in multiple geographic regions. This allows users to deploy resources in different locations, improving performance and redundancy. VPCs can be connected to on-premises data centers using secure and dedicated connections, facilitating hybrid cloud architectures. Virtual Private Clouds are widely used by organizations that require a secure and isolated cloud environment while taking advantage of the scalability and flexibility offered by public cloud services. VPCs play a crucial role in enabling organizations to deploy and manage their applications and services in a controlled and customizable cloud infrastructure.
Advantages: Scalability of public cloud with dedicated resources, cost savings, and flexibility.
Considerations: Relies on the security measures of the public cloud provider.
Converged Infrastructure
Computing, storage, and networking resources are tightly integrated into a single, pre-configured system. This simplifies deployment and management of the private cloud.
Converged infrastructure is an IT infrastructure solution that combines compute, storage, networking, and virtualization resources into a single, integrated system. The goal of converged infrastructure is to streamline and simplify the deployment and management of data center resources, providing a more efficient and cost-effective solution compared to traditional, siloed architectures.
Converged infrastructure integrates various components, including servers, storage arrays, networking equipment, and virtualization, into a single, pre-configured system. Integration simplifies the procurement, deployment, and management of data center resources. It also helps eliminate compatibility issues between different components. Converged infrastructure solutions are typically pre-configured and tested by the vendor, reducing the complexity and time required for deployment. This results in faster time-to-value for organizations.
Converged infrastructure systems often come with unified management interfaces or tools. This allows administrators to manage all integrated components from a single management console, improving operational efficiency. Converged infrastructure solutions are designed to optimize resource utilization. The integrated components work together seamlessly, reducing inefficiencies and ensuring that resources are allocated efficiently. Converged infrastructure is designed to be scalable, allowing organizations to easily add or remove resources as needed. This flexibility supports changing workloads and business requirements.
By consolidating infrastructure components into a single system, converged infrastructure reduces the complexity associated with managing disparate hardware and software elements. This simplification can lead to lower operational costs. Converged infrastructure can lead to cost savings by reducing the need for extensive customization, streamlining management processes, and minimizing the time and effort required for deployment. Converged infrastructure solutions are often provided by specific vendors or partnerships between multiple vendors. This may result in a level of vendor lock-in, so organizations need to carefully evaluate compatibility and future expansion options. Converged infrastructure is well-suited for various use cases, including virtualized environments, private cloud deployments, and applications with predictable workloads.
Converged infrastructure is a response to the challenges posed by the traditional siloed approach to data center architecture. By providing an integrated and unified solution, organizations can achieve greater operational efficiency, faster deployment times, and improved resource utilization. It is particularly beneficial for organizations seeking a turnkey solution to simplify their IT infrastructure.
Advantages: Improved scalability, resource efficiency, and simplified management.
Considerations: May require careful planning for scalability.
Organizations may choose the private cloud deployment model that aligns best with their specific needs, budget, and technical requirements. The choice often involves a trade-off between control, customization, and the level of responsibility handed over to external service providers.
To get detailed info check the below link:-
Private Cloud Deployment Model
Community Cloud Deployment Model
THANK YOU--VISIT AGAIN--
4 thoughts on “Private cloud deployment models-it’s characteristics.”