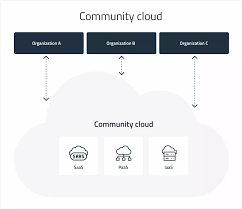
Community Cloud Deployment Model
The community cloud deployment model is a type of cloud computing environment that is shared by multiple organizations with similar interests, requirements, or compliance needs. It is designed to cater to the specific needs of a community of users who collaborate and share common concerns, such as regulatory requirements, security standards, or industry-specific challenges.
Shared Infrastructure
The practice of multiple users or tenants utilizing the same physical computing resources, such as servers, storage, and networking components. This sharing of infrastructure is a fundamental characteristic of cloud deployment models, including public, private, and community clouds.
Cloud providers pool computing resources to serve multiple customers. These resources, including processing power, memory, and storage, are dynamically allocated based on demand. Resource pooling enables efficient utilization and optimization of hardware resources. Shared infrastructure supports a multi-tenant environment where multiple users or organizations coexist on the same physical hardware. While logically separated, the underlying physical infrastructure is shared to achieve economies of scale.
Shared infrastructure contributes to cost efficiency as the operational and capital costs associated with hardware and maintenance are distributed among multiple users. Users benefit from the ability to access advanced infrastructure without the need for significant upfront investments. The shared nature of infrastructure allows for on-demand scalability. Users can easily scale their resources up or down based on changing requirements without the need to procure or decommission physical hardware.
Shared infrastructure enables dynamic allocation of resources based on demand. This dynamic nature allows for optimal resource utilization, with the ability to allocate additional resources during peak usage and release resources during periods of lower demand. While multiple users share the same physical infrastructure, isolation mechanisms are in place to ensure that each user’s data and applications are logically separated. Virtualization technologies, such as hypervisors, help create isolated instances or virtual machines for each user.
Shared infrastructure provides flexibility in resource allocation. Users can quickly provision and de-provision resources, adjusting their computing capacity based on changing requirements. Resources are dynamically allocated based on the current needs of users. This dynamic allocation ensures that resources are efficiently distributed and utilized, minimizing wastage. Load balancing mechanisms are often implemented to distribute workloads evenly across shared resources. This helps prevent bottlenecks and ensures optimal resource utilization.
To maintain security and isolation between different users or tenants sharing the infrastructure, cloud providers implement robust isolation mechanisms. Virtualization and containerization technologies play a crucial role in achieving this isolation. Shared infrastructure enables scalability, allowing cloud environments to handle varying workloads. Users can scale resources horizontally or vertically to accommodate changes in demand. In the case of public and community clouds, the shared infrastructure is often distributed across multiple data centers globally. This allows for global accessibility and low-latency access for users in different geographic locations.
Common Interests
“Common interests” in the context of cloud computing, especially in the community cloud deployment model, refers to the shared objectives, requirements, or concerns that bring together a group of organizations or users to collaborate within a specific cloud environment. These common interests are the basis for forming a community of users with similar needs.
Organizations in a community cloud often share a common industry focus. For example, healthcare organizations might collaborate in a community cloud to address industry-specific challenges and compliance requirements. Common interests may revolve around regulatory compliance. Organizations within the community may have similar compliance requirements and collaborate to ensure that the community cloud meets these standards. Security concerns and standards can be a common interest. Organizations sharing sensitive data or operating in regulated environments may come together to implement and enforce security measures in the community cloud.
Organizations with similar data privacy requirements may join a community cloud. This is especially relevant when dealing with sensitive information that must adhere to specific privacy standards. Common interests may include collaborative projects or initiatives that require a shared computing environment. This could be research projects, joint ventures, or industry-wide initiatives. Organizations may share common interests in optimizing costs through resource sharing. Pooling resources in a community cloud can lead to cost efficiencies for all participating members.
Similar expectations regarding service levels and performance may drive organizations with common interests to collaborate in a community cloud. They can collectively define SLAs that meet their shared requirements. Common interests in technology standards may bring organizations together. For example, a community of software developers may collaborate in a community cloud environment that supports their preferred development tools and frameworks. Organizations operating in the same geographic region or facing similar geographical challenges may find common interests in using a community cloud with data centers strategically located to meet their needs.
Common interests may also include a focus on operational efficiencies. Organizations in a community cloud may aim to streamline processes, improve resource utilization, and enhance overall operational effectiveness.
Collaboration
Collaboration is a key aspect, allowing community members to share data, applications, and resources while working towards common goals.
Collaboration in the context of cloud computing refers to the cooperative efforts among individuals, organizations, or entities within a cloud environment to achieve common goals, share resources, and enhance overall efficiency. Collaboration is a key aspect of various cloud deployment models, including public, private, and community clouds. Collaboration involves the sharing of computing resources, such as virtual machines, storage, and networking infrastructure, among users or organizations within the cloud environment.
Collaborative efforts are driven by common objectives or goals shared among the entities within the cloud. This could include joint projects, research initiatives, or the pursuit of shared business outcomes. Cloud collaboration enables the sharing of data and information among authorized users. This can improve communication, streamline workflows, and support joint decision-making processes. Cloud platforms often provide real-time collaboration tools, including document sharing, version control, and collaborative editing features. These tools facilitate concurrent work on shared documents or projects.
Cloud environments enable cross-functional collaboration, allowing individuals with diverse skills and roles to work together seamlessly. This is especially relevant in complex projects that require expertise from different domains. Cloud-based communication platforms, such as messaging and video conferencing tools, support real-time interactions among team members, fostering effective communication and collaboration. Cloud computing facilitates collaboration among virtual teams, where members may be geographically dispersed. This allows for a more diverse and global workforce.
Collaboration in the cloud involves implementing robust security measures and access controls to ensure that shared resources and data are protected and only accessible to authorized users. Cloud services offer scalable collaboration tools that can adapt to the changing needs of collaborative projects. This ensures that the infrastructure can support increased collaboration as the user base grows.In a community cloud deployment model, collaboration is a central theme. Organizations within the community share a cloud infrastructure and collaborate based on their common interests, such as industry focus, compliance requirements, or shared initiatives.
Customization
Community clouds often provide a level of customization to meet the specific needs of the user community. This allows organizations to tailor the cloud environment to their particular requirements.
“Customization” in the context of cloud computing, including the community cloud deployment model, refers to the ability to tailor and adapt cloud services, resources, and configurations to meet the specific needs and preferences of individual organizations or users within the community. Customization allows users to configure and optimize the cloud environment according to their unique requirements. Community cloud users can customize the selection of services offered by the cloud provider to match their specific needs. This may include choosing specific software applications, development tools, or infrastructure components.
Users can customize the allocation of computing resources, such as virtual machines, storage, and network bandwidth, based on their workloads and performance requirements. Organizations within the community may have different security requirements. Customization allows users to define and implement their own security policies, access controls, and encryption mechanisms within the shared community cloud environment. Customization is often essential for meeting industry-specific compliance standards. Organizations can configure the community cloud to adhere to regulatory requirements and ensure that data handling practices align with legal and industry standards.
Users can customize application configurations and settings within the community cloud to align with their specific business processes. This includes parameters related to performance, scalability, and user access. Customization extends to defining user permissions and roles within the community cloud. Organizations can configure access controls to ensure that users have appropriate levels of access based on their roles and responsibilities. Organizations often have existing IT systems and applications. Customization enables seamless integration between the community cloud and external systems, ensuring interoperability and a smooth flow of data and processes.
Customization is crucial in the development of automated workflows and orchestration processes. Users can customize scripts, templates, and configurations to automate deployment, scaling, and management of resources within the community cloud. Cloud providers may offer customization options for the user interface, allowing organizations to tailor the look and feel of the management console to enhance the user experience and streamline operations. Customization extends to billing and reporting functionalities. Users can customize cost allocation, reporting formats, and billing details to align with their internal accounting and financial processes.
Security and Compliance
Security measures are implemented to address the specific security and compliance needs of the community. This includes controls to meet industry-specific regulations and standards.
“Security and compliance” are critical considerations in cloud computing, and they play a vital role in the community cloud deployment mode. Implement robust access controls to ensure that only authorized users within the community have access to specific resources and data. Use strong identity management and authentication mechanisms to verify the identity of users and devices accessing the community cloud.
Employ encryption techniques to protect data in transit and at rest, ensuring that sensitive information remains confidential and secure. Implement network security measures, such as firewalls and intrusion detection/prevention systems, to protect against unauthorized access and attacks. Establish an incident response plan to promptly address and mitigate security incidents or breaches. This includes monitoring and logging for suspicious activities.
Ensure physical security measures are in place at data centers hosting the community cloud infrastructure to prevent unauthorized physical access. Conduct regular security audits and assessments to identify vulnerabilities and ensure that security measures remain effective over time. Evaluate and ensure the security practices of the cloud service provider, including their data center security, adherence to industry standards, and commitment to security best practices.

To get detailed info check the below link:-
Private Cloud Deployment Model
Community Cloud Deployment Model
THANK YOU--VISIT AGAIN--
4 thoughts on “Community Cloud Deployment Model-It’s characteristics”